
Prismatic & Pouch Battery Packs
Prismatic and pouch LiIon battery packs reduce weight, cost, and packaging waste while allowing efficient space utilization compared to cylindrical cells, thanks to higher specific energy density. Prismatic cells offer rigid form factors with moderate capacity (20–30 Ah), while pouch cells deliver 90–95% packaging efficiency, though they require room for swelling during cycling.
At a Glance: Prismatic Cells and Pouch Cells
- Engineered for weight-sensitive and compact applications, these battery packs utilize prismatic and pouch cells to optimize volume usage.
- Prismatic cells are suited for structured formats like hybrid and electric vehicle powertrains.
- Pouch cells offer flexibility for consumer, military, and automotive applications, provided that swelling is managed in design.

Overview of Prismatic and Pouch Battery Packs
Prismatic Cells
- Introduced in the early 1990s to meet demand for thinner, cost-effective designs, resembling small boxes or bars.
- Found in mobile phones and larger applications as capacities scale from 400 mAh–2,000 mAh up to 20–30 Ah in welded aluminum housings.
- Internal electrodes are either stacked or flattened rolls in a rectangular can.
- Offer better space utilization but with slightly higher manufacturing cost, marginally lower energy density, less efficient thermal management, and vulnerability to shorter cycle life than cylindrical cells.
 Prismatic Cell Battery Packs
Prismatic Cell Battery Packs
| LFP Prismatic Cells | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN# | 2614897-Fe-40 | 3914897-Fe-50 | 26148129-Fe-50 | 54173200-Fe-200 | 71173200-Fe-275 | |
| Typical Capacity (Ah) @0.2C | 40 | 50 | 50 | 200 | 275 | |
| Nominal Voltage (V) | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | |
| Dimension (mm) | 148*27*97 | 148*40*103 | 148*27*129 | 173*53*207 | 173*71*207 | |
| Weight (g) | 0.86 | 1.15 | 0.86 | 4.1 | 5.2 | |
| Internal Resistance (mΩ) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | |
| Discharge | Continuous Discharge | 3C | 3C | 3C | 3C | 3C |
| Charge | Standard | 0.5C | 0.5C | 0.5C | 0.5C | 0.5C |
| Max. | 1C | 1C | 1C | 1C | 1C | |
| End Voltage (V) | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 | |
| Temperature | Charge | 0~45°C | 0~45°C | 0~45°C | 0~45°C | 0~45°C |
| Discharge | -20~60°C | -20~60°C | -20~60°C | -20~60°C | -20~60°C | |
| Life Cycle | 2000 cycles | 2000 cycles | 2000 cycles | 2000 cycles | 2000 cycles | |
Pouch Cells
- Introduced in 1995, pouch cells use conductive foil tabs sealed in flexible envelopes for positive and negative terminals.
- Deliver 90–95% packaging efficiency by eliminating rigid metal enclosures—but require external support.
- Lightweight and flexible, but more susceptible to humidity, heat, external mechanical damage, and thermal-induced swelling.
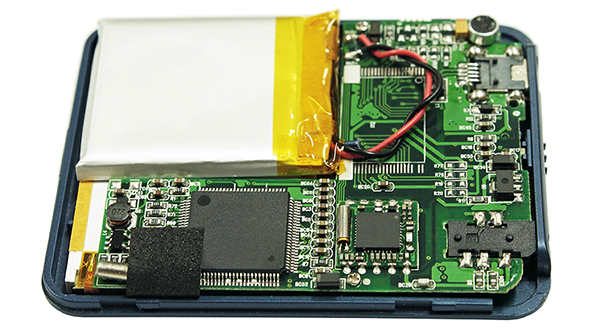 Pouch Cell Battery Pack Inside Application
Pouch Cell Battery Pack Inside Application
| LFP Pouch Cells | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN# | F706094 | F134295 | F7075130 | F1046148 | F1187021 | |
| Typical Capacity (Ah) @0.2C | 2.5 | 3.3 | 4.5 | 6 | 8 | |
| Nominal Voltage (V) | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 | |
| Dimension (mm) | 96*61*7.2 | 97*43*13 | 132*76*7.1 | 150.47*10 | 127*88*21 | |
| Weight (g) | 75 | 97 | 130 | 146 | 225 | |
| Internal Resistance (mΩ) | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3.5 | |
| Discharge | Continuous Discharge | 30C | 30C | 30C | 30C | 30C |
| Pulse Discharge | 60C 2S | 60C 2S | 60C 2S | 60C 2S | 60C 2S | |
| End Voltage (V) | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | |
| Charge | Standard | 0.5C | 0.5C | 0.5C | 0.5C | 0.5C |
| Max. | 1C | 1C | 1C | 1C | 1C | |
| End Voltage (V) | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.6 | |
| Temperature | Charge | 0~45°C | 0~45°C | 0~45°C | 0~45°C | 0~45°C |
| Discharge | -20~60°C | -20~60°C | -20~60°C | -20~60°C | -20~60°C | |
| Life Cycle | 2000 cycles | 2000 cycles | 2000 cycles | 2000 cycles | 2000 cycles | |
Key Trade-offs
- Packaging Efficiency: Pouch cells achieve up to 95%, while prismatic cells are less efficient but more structurally rigid.
- Mechanical Durability: Prismatics have welded metal cases for structural integrity; pouch cells require added support to avoid damage.
- Thermal & Lifecycle Performance: Prismatic cells feature better thermal management but lower specific energy; pouch cells may suffer more from heat and humidity.
- Swelling Considerations: Pouch cell gases cause 8–10% swelling over 500 cycles; design must account for expansion.
Managing Swelling in Pouch Cell Packs
- Swelling results from gas generation during charge/discharge.
- Cells can expand 5 mm → 8 mm or 8–10% thickness increase across cycles.
- Manufacturers include excess film (“gas bag”) to capture gases initially, then seal the pack.
- Pack design must allow space for expansion, avoid stacking, and eliminate sharp edges to prevent damage.
Applications
- Prismatic packs: Ideal for electric/hybrid vehicle powertrains and portable electronics where compactness meets structural needs.
- Pouch packs: Common in consumer, military, and automotive electronics; Lipolymer chemistry delivers light, flexible designs.
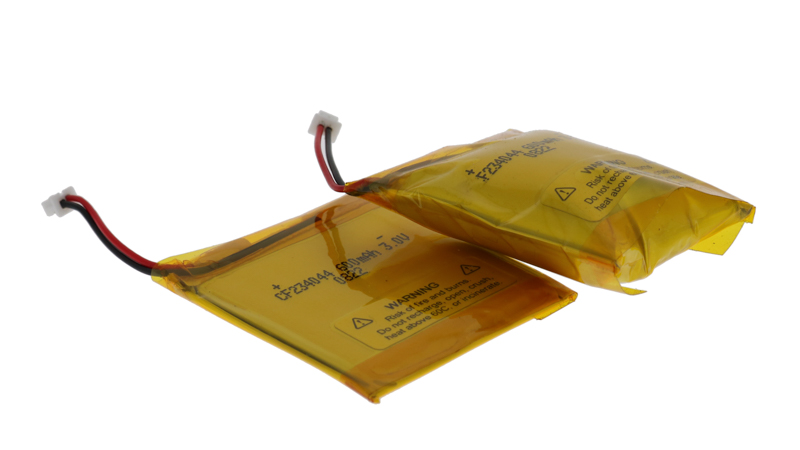 Swelling Pouch Cell Battery as a Result of Gas Generation During Charge and Discharge
Swelling Pouch Cell Battery as a Result of Gas Generation During Charge and Discharge
Frequently Asked Questions
Quick Links
- What cells are packaged in welded aluminum housings?
- What causes swelling in pouch cell batteries?
- How much packaging efficiency do pouch cells provide?
- What discharge rates do pouch cells support?
- What is the typical cycle life for these batteries?
What cells are packaged in welded aluminum housings?
Prismatic cells are typically enclosed in welded aluminum housings, offering capacities of 20–30 Ah.
What causes swelling in pouch cell batteries?
Swelling occurs due to gas generation during charge and discharge, which can increase cell thickness by 8–10% over cycles.
How much packaging efficiency do pouch cells provide?
Pouch cells offer packaging efficiency of 90–95%, the highest among battery pack designs.
What discharge rates do pouch cells support?
Pouch cells support continuous discharge rates of 30C and pulse discharge of 60C for 2 seconds.
What is the typical cycle life for these batteries?
Both prismatic and pouch cells are rated for approximately 500 charge/discharge cycles.
What’s Best For Your Application?
Make the right choice for your battery needs. Discover the advantages of nickel metal hydride battery packs vs lithium packs. Explore the benefits of each battery chemistry in your application. Ensure longevity with cost-effective BMS solutions.
Request a Quote Request Design Support Request More Information








