
Battery Management Systems
Battery management systems (BMS) mean different things to different people. At Epec BMS is simply constant monitoring of key operational parameters during charging and discharging using outputs from sensors which give the actual status of voltages, currents, and temperatures within the battery as well as the state of charge. See how this applies to The Role of the Battery Management System.
At a Glance: Battery Management Systems
- Monitors and controls critical functions such as voltage, current, and temperature to maintain safe and efficient operation.
- Prevents overcharging, over-discharging, and thermal issues while balancing cells to extend battery life.
- Provides communication capabilities for real-time data and diagnostics in advanced systems.
Custom Manufactured BMS Solutions
Since we have developed our own unique battery management system we don’t have to rely on 3rd parties for battery management system design as a lot of other companies do.
Our state of the art BMS integrates a precise battery gauge, cell balancing, protection circuitry, system control firmware and other safety features like temperature protections that will not allow charging outside of a specified temperature range.
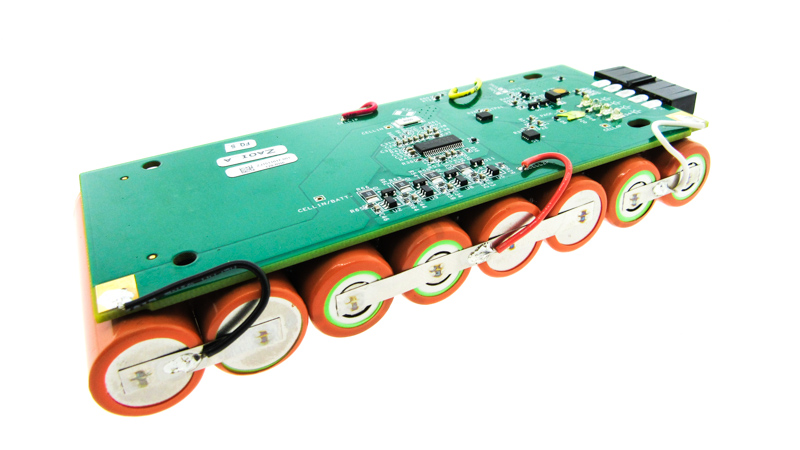
This is done by utilizing a microcontroller to manage information from the sensing circuitry and then make decisions with the received information using application specific algorithms that are digitally encoded into the microcontroller. Working closely with some of the key integrated circuit (IC) manufactures in the industry such as Texas Instruments (TI), Linear Technologies and Sieko, we safely and cost effectively build some of the most creative designs in the industry.
How We Customize A BMS for Each Application
In order to control battery performance and safety it is necessary for an in-depth understanding of the fundamental application requirements that the battery needs to meet. From there we can move into putting all of the building blocks in place.
BMS Critical Components
Every BMS performs 3 critical functions for every application.
- Provides protection for the cells, the battery pack and the pieces of equipment that it is powering as a thermal runaway in a battery pack can cause significant damage.
- Extends the life of the battery by managing how and when it is used which minimizes the number or charge/discharge cycles.
- Keeps the battery in a state so that it is constantly prepared to power the application the moment it becomes necessary.
Additional BMS Functions That Can Be Incorporated
- Cell Protection: Lithium ion cells have two critical design issues; if you overcharge them you can damage them and cause overheating and even explosion or flame so it is important to have a battery management system to provide overvoltage protection and they can also be damaged if they're discharged below a certain threshold, approximately 5 percent of total capacity. If the cells are discharged below this threshold their capacity can become permanently reduced.
- Charge control: All batteries have a useful number of charge/recharge cycles so managing this function efficiently is critical to the life of the battery back. Along with that, overcharging is the most harmful thing that can happen to any battery.
- Demand Management: The objective of any battery pack design is to minimize the current drain on the battery to lengthen the battery life by implementing power saving techniques into the BMS circuitry. This requires a many years of design experience and a library of designs to pick and choose the right tools from.
- SOC Determination: Many applications require knowledge of the State of Charge (SOC) of the battery or of the individual cells in the battery chain. This may simply be for providing the user with an indication of the capacity left in the battery, or it could be needed in a control circuit to ensure optimum control of the charging process. In many applications this is the first reading to the control board as a device may have a minimum SOC for effective use.
- SOH Determination: An important aspect of battery diagnostics is the battery state of health (SOH) determination which is a qualitative measure of the battery’s ability to store energy and deliver power. Battery diagnostics track the degradation of battery’s performance to estimate battery SOH.
- Cell Balancing: A battery pack usually consists of several individual cells that work together in combination. Ideally, all the cells in a battery pack should be kept at the same state of charge. If the cells go out of balance, individual cells can get stressed and lead to premature charge termination and a reduction in the overall cycle life of the battery. The cell balancing function extends the life of the battery by preventing this imbalance of charge in individual cells from occurring. While this functionality is not necessary in every application as it adds cost, we make it standard in all of our designs.
- History - (Log Book Function): Being able to write data about the performance of the battery pack is another possible function of the BMS. This is an important tool in determining state of health (SOH) of the battery, usage data for next generation designs and in assessing warranty claims.
- Authentication and Identification: Being able to write information to the battery pack hardware allows OEM’s to serialize, lot number control, and provide any other traceability that an application requires.
Frequently Asked Questions
Quick Links
- What is the primary function of a battery management system?
- How does a BMS protect against overcharging?
- Why is cell balancing important?
- Does a BMS monitor temperature?
- Can a BMS provide communication capabilities?
- What happens if a battery is over-discharged?
What is the primary function of a battery management system?
The primary function of a battery management system (BMS) is to monitor and regulate key parameters such as voltage, current, and temperature across the battery pack. By continuously tracking these values, the BMS ensures that the battery operates within safe limits and prevents conditions that could lead to failure or hazards. It also manages charge and discharge cycles to optimize performance and longevity. This level of control is critical for maintaining reliability in applications where batteries are a core power source.
How does a BMS protect against overcharging?
A BMS prevents overcharging by monitoring the voltage of individual cells and the overall pack during the charging process. When cells approach their maximum allowable voltage, the system limits or stops charging to avoid exceeding safe thresholds. Overcharging can cause overheating, chemical degradation, and even thermal runaway, so this safeguard is essential for safety. By controlling the charging process, the BMS helps maintain battery health and extends its usable life.
Why is cell balancing important?
Cell balancing ensures that all cells within a battery pack maintain similar voltage levels, which is critical for efficiency and longevity. Without balancing, some cells may become overcharged or over-discharged, leading to uneven wear and reduced capacity over time. The BMS uses active or passive balancing techniques to redistribute energy and keep cells aligned. This process not only improves performance but also minimizes the risk of failure due to cell imbalance.
Does a BMS monitor temperature?
Yes, temperature monitoring is a key function of a BMS because excessive heat can damage cells and create safety hazards. The system tracks temperature during both charging and discharging cycles to detect abnormal conditions early. If temperatures rise beyond safe limits, the BMS can reduce current flow or shut down the system to prevent thermal runaway. This proactive approach helps maintain safe operation and protects the battery from irreversible damage.
Can a BMS provide communication capabilities?
Advanced BMS designs often include communication interfaces that allow real-time data exchange with external systems. These interfaces can transmit information such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge to controllers or monitoring platforms. This capability enables diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and integration with larger systems like electric vehicles or industrial equipment. By providing visibility into battery health, communication features enhance reliability and operational efficiency.
What happens if a battery is over-discharged?
Over-discharging occurs when a battery’s voltage drops below its safe minimum level, which can permanently damage cells. The BMS prevents this by disconnecting the load or signaling a shutdown when voltage approaches critical thresholds. This protection helps avoid chemical degradation and capacity loss that result from deep discharge. By managing discharge limits, the BMS ensures the battery remains functional and safe throughout its service life.
Need a Custom Battery Management System?
Experience constant monitoring and customization with our state-of-the-art battery management systems. Contact us to maximize safety, longevity, and performance for your application!
Request a Quote Request Design Support Request More Information








