
Embedded Resistors in Hi-Speed PCBs
High-speed printed circuit boards (PCBs) can be found everywhere. From the smartphones and the medical devices to military radars and satellites up in space, printed circuit boards allow electronics to perform specific functions and tasks to better our lives.
In the past, circuit boards had simplified integrated circuits (ICs) that only consisted of a few transistors and a resistor. This simple design was suitable for electronics decades ago, which did not require high-speed capabilities or were required to perform multiple functions. As technology progressed, electronics were required to do more as ICs became more complex. Hundreds to tens of millions of transistors were placed into printed circuit chips.
One hurdle that PCB manufacturers faced was the miniaturization of electronics. In this age, a device is smaller and lightweight enough to be mobile. This factor leaves less room available for the complex ICs inside the electronics’ housing as passive and active parts need adequate space to function without lessening the integrity of the printed circuit board. To deal with this issue, passive components became embedded into the printed circuit boards. Now, and for the past 10 years, manufacturers can use embedded resistor printed circuit boards, as well as embedded capacitors and inductors.
In this space there are 2 major players who design and manufacturing the leading-edge substrates for this technology. Ticer Technologies and Ohmega Technology manufacture high-performance, thin-film embedded resistor copper foil which gives us many different options for every application. Epec Engineered Technologies has experience with both manufacturers and we can assist in developing the best solution to your needs.
Dive deeper into Using Embedded Resistors and Specialized High-Speed PCB Materials.
Embedded Resistors Offering Benefits vs. SMTs
Surface mounted resistors (SMTs), have small rectangular ceramic bodies with metalized ends that are contacts. The printed circuit board will have pads where the ends of the SMTs will form the connection. On the other hand, embedded resistors are planar resistive elements made into a thin film. This type of resistor becomes part of the etched and printed circuitry on the standard printed circuit board layer as it eliminated the need for solder joints. Advantages that are gained when using embedded resistors include the below.
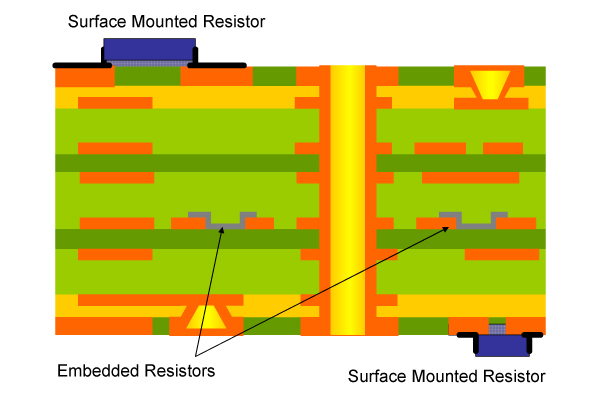
Increased Routing Area
By removing discrete SMTs from the circuit boards, there is less room used up by the interconnecting traces and vias. The embedded resistor allows for more space to be available on the printed circuit board, which manufacturers can then add other functions or reduce the size of the printed circuit board for smaller applications and devices.
Shorter Wiring Lengths
The wiring length from the passive components can become complex with connecting to the integrated circuits for discrete SMTs. With no vias being needed for embedded resistors and by improving the routing, manufacturers can cut down on their operational costs while still being able to provide complex printed circuit boards for a variety of applications. This creates more simplified boards that come in a smaller size and are more compact.
Reduction in Electromagnetic Interference and Parasitic Effects
Circuitry and components will have different electrical fields. When these circuits are placed close to each other, they begin to store up an electrical charge. This electrical charge can have negative effects (parasitic capacitance) as it can change the intended output of the circuits. In addition, electromagnetic emissions from external sources in direct contact or when emitted (induction) can create electromagnetic interference (EMI) that will impact the functionality of the printed circuit board.
Embedded resistors can reduce parasitic capacitance, EMI, cross talk, and noise generated by other components and circuitry near the printed circuit board. The embedded resistor technology can be placed under the pin of the integrated circuit to avoid inductance and ensure better electrical performance.
Enhanced Integrity
The overall integrity of the printed circuit board is enhanced when resistors are embedded into the board. This manufacturing process allows for more stability over wider frequencies, an increased lifecycle of the printed circuit board, and lower the signal reflection from the load due to improved line impedance matching.
Embedding Resistors Using OhmegaPly®
Epec works with Omega Technologies Inc and there OhmegaPly® product to embed resistors into printed circuit boards. OhmegaPly® is a thin film electrodeposited-on-copper NiP metal alloy (Resistor Conductor Material) that is laminated to a dielectric material and subtractively processed to produce planar resistors. Because of its thin film nature, it can be buried within layers without increasing the thickness of the board or occupying any surface space like discrete resistors. The OhmegaPly® product is unique because it has a low RTC of <;50ppm, it is stable over a wide frequency range as it tested beyond 20GHz, and it has a superior life-testing performance at >100,000 hours +2% at 110C.
Some applications that we have worked on are surface resistors on HDI circuit boards, embedded pull up resistors in aerospace applications, series, and parallel termination resistors in a BGA package and may more.
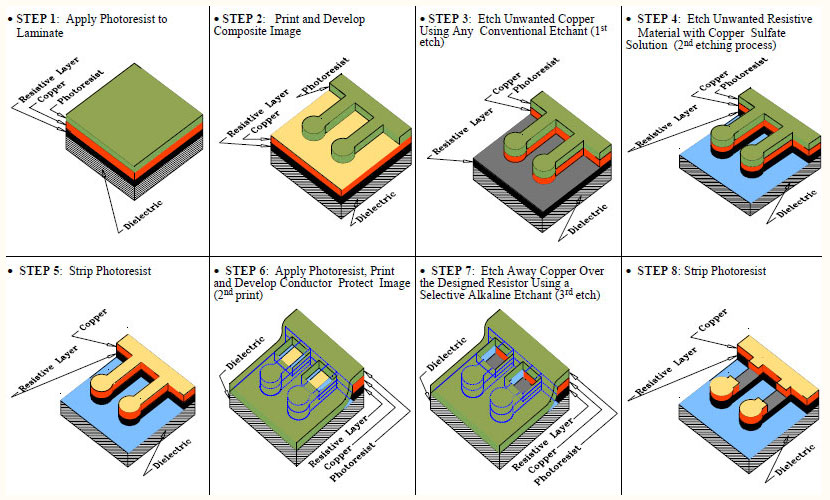
Simplifying the PCB Subtractive Manufacturing Process
While the process may look familiar to the traditional PCB subtractive manufacturing process it is far from that. The two biggest things that fabricators need is:
- In order to etch the resistive OhmegaPly® it needs to be done in a copper sulfate solution and then the copper must be etched away over the resistor using an alkaline etchant which are both unique process that must be invested in to be able to effectively use OhmegaPly® for embedded resistors.
- CAD operators need to be trained as problems in embedded passive designs have to do with the difference between thick film additive and thin film subtractive technologies. Resistor elements and terminations are determined by different techniques for additive than for subtractive processes.
How to Best Specify Embedded Resistors in Your Gerber Data
All of the material manufacturers have their standard design parameters for long-term stability and how to best manage the tolerance requirements for each design. Engineering teams here at Epec will work with you to design the best-in-class features that will ensure that your design meets your specifications. Mentor graphics has an effective platform for the design of embedded passive components.
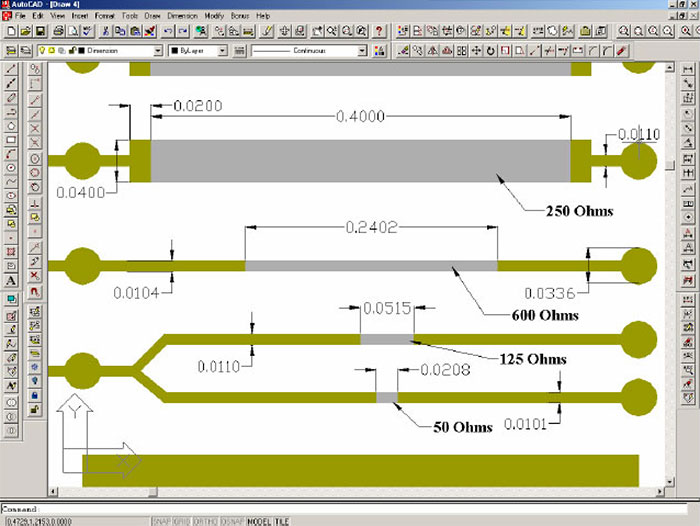
Embedded Passive Standards
- IPC-4821 Specification for Embedded Passive Device Capacitor Materials
- IPC-4811 Specification for Embedded Passive Device Resistor Materials
- IPC-2316 Design Guides for Embedded Passive Device Printed Boards
- IPC-6017 Qualifications and Performance Specifications for Printed Boards Containing Embedded Passives
Learn More About Embedded Resistors from Epec
Here at Epec, we provide a wide range of printed circuit boards for a variety of industries. As electronics become smaller and more advanced, our clients look for cost-effective components and faster time-to-market solutions. Embedded resistors can provide a range of advantages for applications requiring high-speed printed circuit boards.
Contact our engineers today to discuss this technology and how your application may benefit from it.
Looking for Embedded Resistors in Your PCB?
Unlock the full potential of your high-speed applications with our expertise in embedded resistors in your circuit boards. Consult with our engineers now for tailored solutions.
Request a Quote Request Design Support Request More Information









