
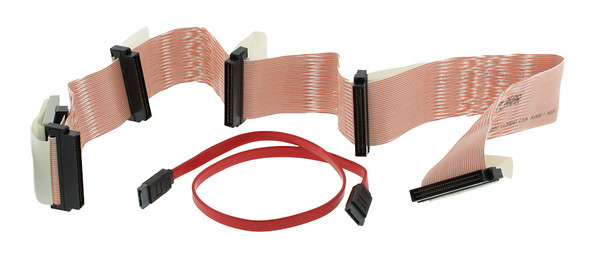
Flat Ribbon Cable Assemblies
Ribbon cable, a.k.a. flat ribbon cable or planar cable, is a cable designed in a flat and rectangular shape and gets its name from its resemblance to a piece of ribbon. A ribbon cable is made of conductors or wires running next to or parallel to each other on the same flat plane and as a result the cable is wide and flat.
For most simple point-to-point ribbon cable assemblies, you can buy the components from online distributors and build them yourself. Epec focuses on more complex ribbon cables that require custom bends or folds, soldering or custom terminations, or other complex nonstandard requirements.
See our blog post that outlines the guide to ribbon cable assemblies for more information.
Flat Ribbon Cable Benefits
The most beneficial characteristic of a ribbon cable is that it is flat and flexible. This flexibility is extremely useful and allows a ribbon cable to be easily routed in confined spaces or in applications where there is limited space to connect two components together. To make installation easier, to align the cable conductors to certain pins on the connector, and to reduce the risk of reversed connections, ribbon cable is typically color coded or edge marked for orientation.
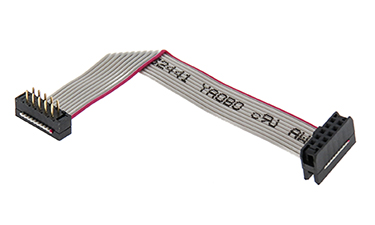
Folded Flat Ribbon Cable Assemblies
Flat and ribbon cables can be folded into a custom configurations where spacing constraints are a limiting design factor. When folding is preferred at assembly, cables are pre-creases limit the stress cables normally endure from standard folding processes.
By having Epec fold your cables as part of our assembly process you can reduce your final costs as the cables arrive ready to use in your assembly.
Folding cables requires specific tooling and equipment in order to make sure the folds are complete and permanent.
Color Coded Ribbon Cables
A color coded ribbon cable, a.k.a. as a rainbow ribbon cable or twist and flat, uses a repeating pattern of colors as the identification for the conductors.
This pattern typically uses the industry standard resistor color code where brown would be used for conductor and pin 1, 11, and 21, red being used for conductor and pin 2, 12, and 22, etc. The color coded ribbon cables can consist of insulated conductors pulled in parallel to each other or be manufactured with twisted pairs where there is a repeating flat section for termination on specific length intervals.
An edge marked cable is usually marked with a stripe on the first conductor which is connected to pin 1 on the connector. The edge marking can be any color, but typically is based on the pitch or center spacing of the cable. For instance 0.050” pitch cable is typically red edge marked. This method of identification is suitable for cables that consist of two or more IDC connectors with every connector connecting to every wire, but is somewhat less helpful when individual wires or small groups of wires must be terminated separately. In this case there would be additional marking applied to specified conductors to allow for proper identification and termination.
Flat Ribbon Cable Applications
Ribbon cables are usually used as interconnects for internal peripherals in computers, such as hard drives, CD drives, and floppy drives. On some older computer systems they were also used for external connections. Unfortunately the ribbon-like shape interferes with computer cooling by disrupting airflow within the computer case which has limited the use of ribbon cables in computer designs recently. Round cables have almost entirely replaced ribbon cables for external connections and are increasingly being used internally as well.
When first launched, ribbon cables were utilized in the mainframe computer industry, on card readers, card punching machines, and tape machines. As ribbon cables became more widely used, manufacturing methods and materials were developed to simplify and reduce the cost of ribbon cables. This standardization in the design and spacing of the wires allowed this family of cables to be easily terminated through the use of Insulation Displacement Connectors, or IDC connectors. Because of the simplicity of ribbon cables, their low profile, and low cost due to standardization, ribbon cables are used today in most computers, printers, and many electronic devices.
Ribbon Cable Specifications
Ribbon cables are typically specified by two numbers: the spacing or pitch of the conductors, and the number of conductors or ways.

A spacing of 0.050 inch is the most common spacing, but finer and courser pitch cables are also available, from 0.025 inch to 0.156 inch with custom spacing available depending on specific applications. In some portable electronic equipment, cable with a pitch as low as 0.3mm can be found.
Because of the availability of standard connectors, the number of conductors or ways is usually restricted to a few values. These include 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 14, 15, 16, 18, 20, 24, 25, 26, 34, 37, 40, 50, 60, 64 and 80. The wire used in ribbon cables is usually stranded copper wire in sizes ranging from 18 AWG to 34 AWG or finer.
Ribbon Cable Advantages
The biggest advantage of ribbon cables is to allow mass termination to specially designed insulation-displacement connectors (IDC), although ribbon cables can also be terminated by using crimp contacts or solder-bucket connections. The IDC termination methodology allows the conductor of an insulated wire or cable to make contact by a connection process which forces a sharpened blade through the insulation, eliminating the need to strip the wire of insulation before connecting. IDC connectors are categorized by pin spacing, number of pins, and number of rows.
Need Custom Ribbon Cables?
Maximize flexibility and performance with Epec's custom ribbon cable assemblies. Ideal for complex, space-constrained applications.
Request a Quote Request Design Support Request More Information








